What is Environmental Justice?
Environmental Justice (EJ) is the fair treatment and meaningful involvement of all people regardless of race, color, national origin, or income in the development, implementation, and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations, and policies.
What is the relationship between environmental justice and climate change?
Climate change is an environmental justice issue because certain groups of people in the United States are disproportionately affected by climate change and are less able than others to adapt to or recover from climate change impacts. These groups include people of color, low-income communities, immigrants, and people who are not fluent in English.
Climate change and health factors
There are many factors that can affect someone’s ability to prepare for, respond to, and cope with the impacts of climate change on health. These include:
- living in areas particularly vulnerable to climate change (like communities along the coast)
- coping with higher levels of existing health risks when compared to other groups
- living in low income communities with limited access to healthcare services
- having high rates of uninsured individuals who have difficulty accessing quality healthcare
- having limited availability of information and resources in a person’s native language
- less ability to relocate or rebuild after a disaster
Environmental Justice at HHS
HHS is dedicated to working with our private and public partners to provide an environment where all people enjoy the same degree of protection from environmental and health hazards and equal access to the decision-making process to maintain a healthy environment in which to live, learn, and work. Our Office of Climate Change and Health Equity serves as a coordinating body to make this goal a reality.
- Learn about the threats of climate change on human health. Explore by topic and region.
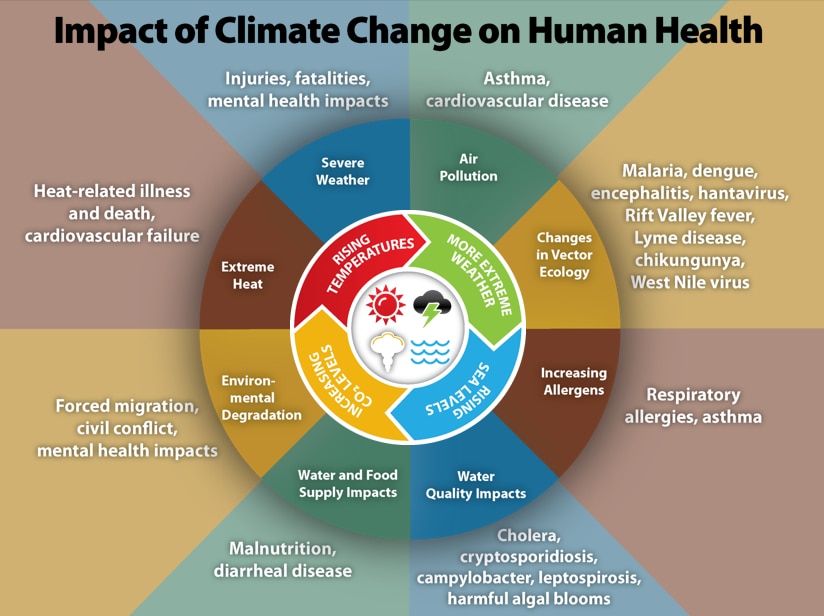
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Four major environmental impacts that will impact human health include:
- Rising Temperatures
- Extreme heat which leads to heat-related illness, cardiovascular failure, and death
- Severe weather which leads to injuries, fatalities, and mental health impacts
- More Extreme Weather
- Air pollution which leads to asthma and cardiovascular disease
- Changes in vector ecology which lead to malaria, dengue, encephalitis, hantavirus, Rift Valley fever, Lyme disease, chikungunya, West Nile virus
- Rising Sea Levels
- Increasing allergens which leads to respiratory allergies and asthma
- Water quality impacts which lead to cholera, cryptosporidiosis, campylobacter, leptospirosis, harmful algal blooms
- Increased CO2 levels
- Water and food supply impacts which lead to malnutrition and diarrheal disease
- Environmental degradation which leads to forced migration, civil conflict, and mental health impacts

